You Tube
Friday, 2 December 2022
Network Error on Shared Folder error code 0x800704cf (network location cannot be reached)
Friday, 25 November 2022
background Image fixed & center with no repeat. you will background fixed and text floating.
Monday, 31 October 2022
Biometric Settings
Friday, 5 August 2022
Replacing Symbols like "&" (Ampersand)
Results = Results.Replace("%", "%25")
Results = Results.Replace("<", "%3C")
Results = Results.Replace(">", "%3E")
Results = Results.Replace("#", "%23")
Results = Results.Replace("{", "%7B")
Results = Results.Replace("}", "%7D")
Results = Results.Replace("|", "%7C")
Results = Results.Replace("\", "%5C")
Results = Results.Replace("^", "%5E")
Results = Results.Replace("~", "%7E")
Results = Results.Replace("[", "%5B")
Results = Results.Replace("]", "%5D")
Results = Results.Replace("`", "%60")
Results = Results.Replace(";", "%3B")
Results = Results.Replace("/", "%2F")
Results = Results.Replace("?", "%3F")
Results = Results.Replace(":", "%3A")
Results = Results.Replace("@", "%40")
Results = Results.Replace("=", "%3D")
Results = Results.Replace("&", "%26")
Results = Results.Replace("$", "%24")
In .net core ver 2.1 ( late 2018 ) I was able to use the following:
System.Web.HttpUtility.UrlEncode(string_to_encode)
Another character that needs escaping is the apostrophe. Replace it with %27.
string url = Server.UrlEncode(value).Replace("'", "%27);
HttpUtility.UrlEncode() And Server.UrlEncode() do not replace this character along with a few others for backwards compatibility with other .Net Frameworks. See this microsoft article for details:
Thursday, 14 July 2022
Network Computers are not Showing Up in Windows 10/11
Network Computers are not Showing Up in Windows 10/11
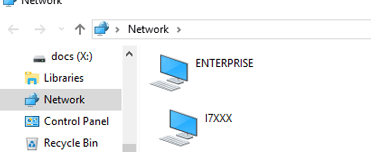
I have received several emails from readers asking for help in resolving the problem of displaying computers in a network environment on the latest Windows 10 and 11 builds. Indeed, there are device network discovery problems in the latest releases of Windows 10: you can’t see other computers on a network, or your Windows 10 is not showing up in the Workgroup environment. Let’s see how to fix the Network Discovery issue in the latest Windows 10 builds (up to 21H2).
Windows Can’t See Other Computers on a Network
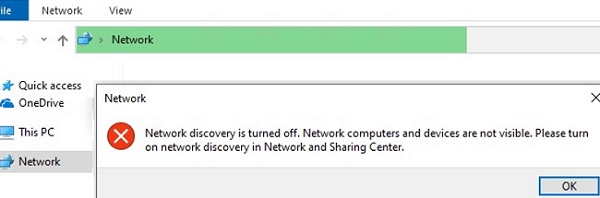
Users are experiencing issues with displaying neighboring computers on the workgroup LAN starting from Windows 10 1703. After installing this (or a newer version of Windows 10), your computer may stop seeing neighboring computers on the network. An error occurs when you try to view the device list in the network by clicking the Network icon in File Explorer:
Network discovery is turned off. Network computers and devices are not visible. Please turn on network discovery in Network and Sharing Center.
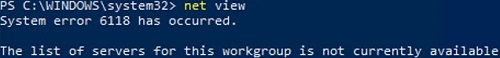
When trying to show a list of computers in the network environment with the net view command, an error appears:
System error 6118 has occurred. The list of servers for this workgroup is not currently available.
Check the following settings to show the network devices on your Windows network:
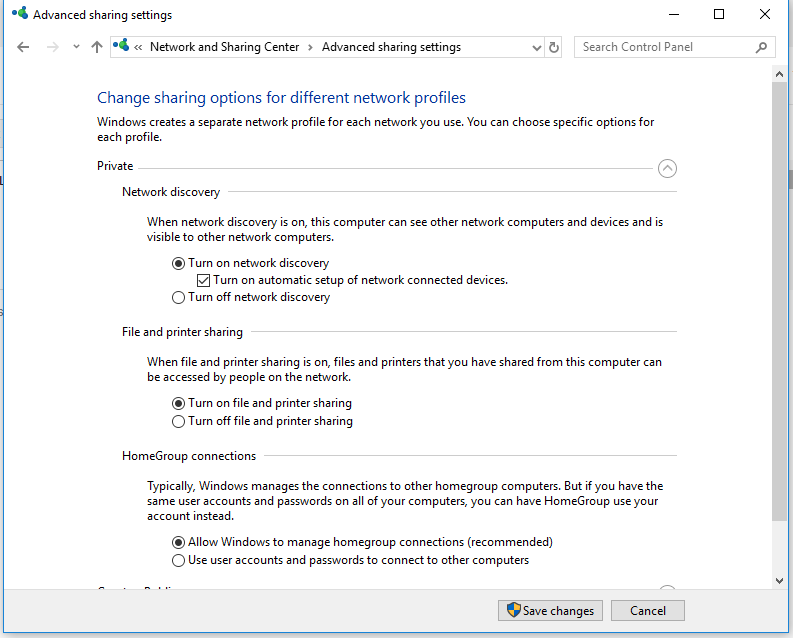
Go to Control Panel -> Network and Sharing Center -> Change advanced sharing settings (you can run the command: control.exe /name Microsoft.NetworkAndSharingCenter /page Advanced).
Make sure that the following options are checked in the Private network profile section:
- Turn on network discovery + Turn on automatic setup of network connected devices;
- Turn on file and printer sharing;
- Allow Windows to manage homegroup connections (recommended).
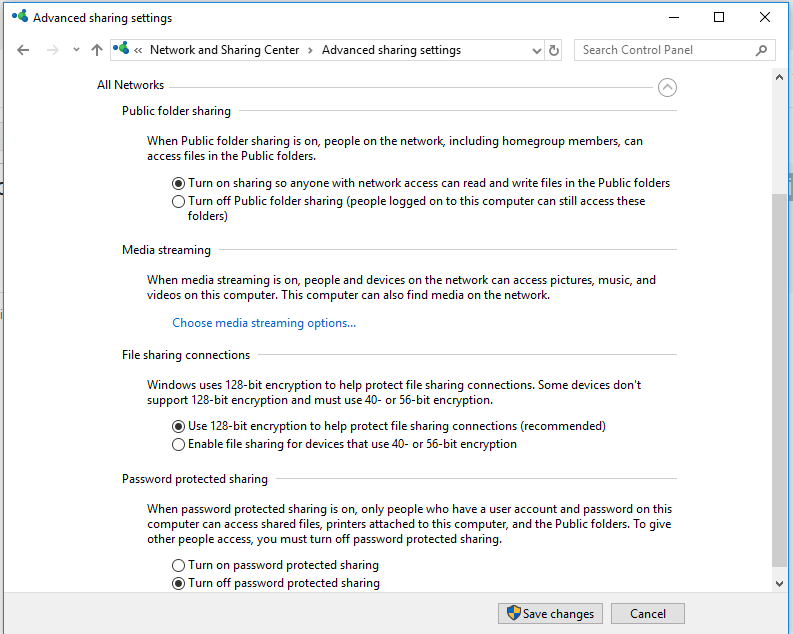
Then enable the following options in the All networks section:
- Turn on Public Folder sharing so anyone with network access can read and write files in the Public folders (optional);
- Turn off password protected sharing (if you trust all the devices in your network);Thus, you can open anonymous network access to your computer. So, when you enable this option, you must correctly set the permissions on the shared network folders and printers.
- If there are legacy network devices in your network (old Windows version, Samba shares, NAS devices), enable the option “Enable file sharing for devices that use 40-bit or 56-bit encryption”.
Then go to Settings -> Network and Internet -> Ethernet (or select Wi-Fi, if you are connected to a local network through a wireless connection). Click the network icon and verify that the Make this PC discoverable option is enabled.
Flush the DNS cache on the computer:
ipconfig /flushdns
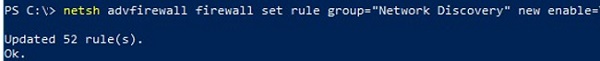
To enable the Network Discovery traffic in Windows Defender Firewall, you must run the following command in the elevated command prompt:
netsh advfirewall firewall set rule group="Network Discovery" new enable=Yes
Get-NetFirewallRule -DisplayGroup "Network Discovery" -Enabled True -Action Allow -Direction Inbound
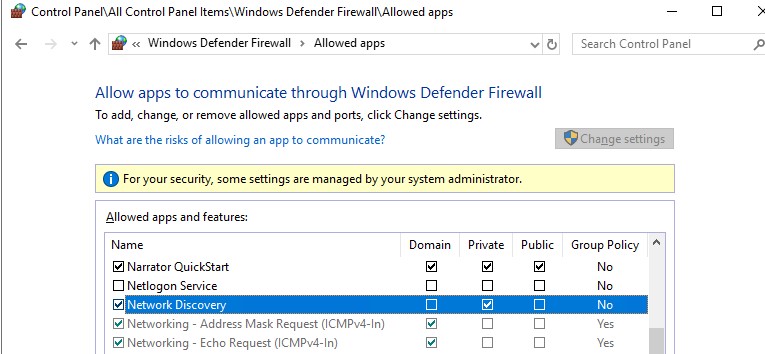
Also, you can manually enable the Network Discovery protocol for at least the Private network in the Windows Defender Firewall settings (Control Panel\All Control Panel Items\Windows Defender Firewall\Allowed apps).
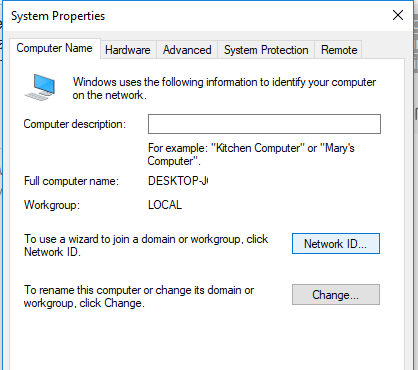
In some cases, Windows computers may not be displayed in the network environment due to incorrect workgroup settings. Try to rejoin this computer in the workgroup. Go to the Control Panel -> System and Security -> System -> Change Settings -> Network ID.
In the Join Domain or Workgroup Wizard that opens, select: This computer is part of a business network -> My company uses a network without a domain -> enter your workgroup name. After that, you need to restart the computer.
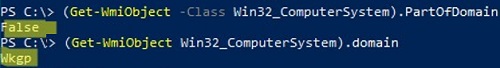
(Get-WmiObject -Class Win32_ComputerSystem).PartOfDomain
(Get-WmiObject Win32_ComputerSystem).domain
In this example, the computer is joined to the WKGP workgroup. To change the computer’s workgroup name to WORKGROUP:
(Get-WmiObject Win32_ComputerSystem).JoinDomainOrWorkgroup("WORKGROUP")
Restart your computer:
Restart-Computer
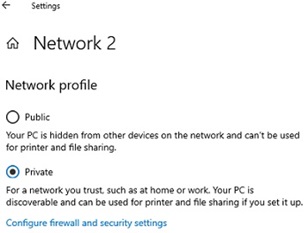
If after rebooting the computer appeared in a network environment, but you can’t access it, check the network profile type (location) on your computer. Most likely your local network was recognized as Public. You need to change the network location to Private. To do this, open the Settings -> Network and Internet -> Status -> select your network connection (Ethernet 2 in my case) and click Properties. Check that the Network Profile is set to Private (if it’s set to Public, change the network type to Private).
Restart your computer, open the Network and check if nearby Windows computers are displayed.
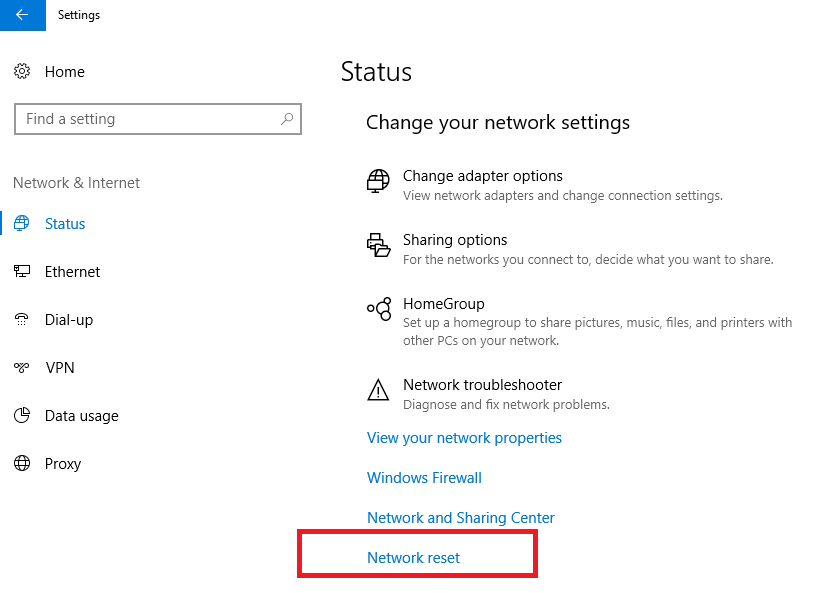
If these tips did not help, and the computers in the workgroup are still not displayed, try to reset the network settings (Settings -> Network and Internet -> Status -> Network Reset).
You can also reset the network settings and Windows Defender firewall rules with the commands:
netsh int ip reset reset.txt
netsh winsock reset
netsh advfirewall reset
Then you need to reboot the computer.
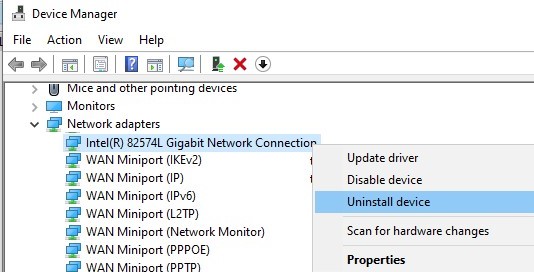
Then restart your computer. Windows should automatically detect your network adapter and install the appropriate drivers. In this case, all old protocol settings for the network adapter will be reset.
Also, check whether the following services are running (they should be in the automatic startup state to correctly display your network environment). Run the services.mcs console and check the services state:
- FdPHost – Function Discovery Provider Host (responsible for discovering other computers on the network);
- FDResPub – Function Discovery Resource Publication (allows other computers to discover your device on the network);
- Dnscache – DNS Client;
- SSDPSrv – SSDP Discovery;
- Upnphost – PnP Device Host.
In some cases, third-party antiviruses, firewalls, or VPN clients can block NetBIOS name resolution requests, WDS, and broadcast DNS queries (there was definitely a problem with ESET NOD32). Try to temporarily disable your antivirus/firewall/VPN and check if the network discovery works properly on your Windows device.
How to Enable Network Discovery on Windows 10 and 11?
Starting with Windows 10 1803 (Spring Creators Update), Microsoft developers removed the ability to create a HomeGroup. In addition, other Windows 10 and Windows 11 computers are no longer displayed in the network environment of File Explorer when viewing network devices.
From Microsoft’s point of view, a HomeGroup is a legacy way to create a local area network to share folders and printers. Instead of using a WorkGroup, Microsoft suggests using its cloud services (OneDrive or access through Microsoft Accounts).
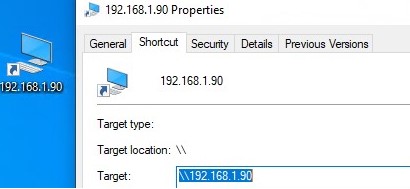
In order to access the shared resources on another computer over the local network from a Windows 10 device, you need to know its hostname (\\pcname1) or IP address (\\192.168.1.90), but neighboring computers in the network are not displayed. However, this can be fixed.
The thing is that a separate Function Discovery Provider Host service is responsible for discovering neighboring computers on a Windows 10 network. Another service, Function Discovery Resource Publication, is responsible for discovering your computer.
These protocols replace the NetBIOS over TCP/IP, which has historically been used to discover devices on Microsoft Windows networks with Master Browser. Accordingly, you can safely disable the NetBIOS protocol for your network adapters.
After installing the latest Windows 10 builds, these services can be disabled (the startup type changed from Automatic to Disabled). If these services are stopped, the computer is not discovered on the network by other computers and cannot see others. You can enable the network discovery services in Windows 10 as follows.
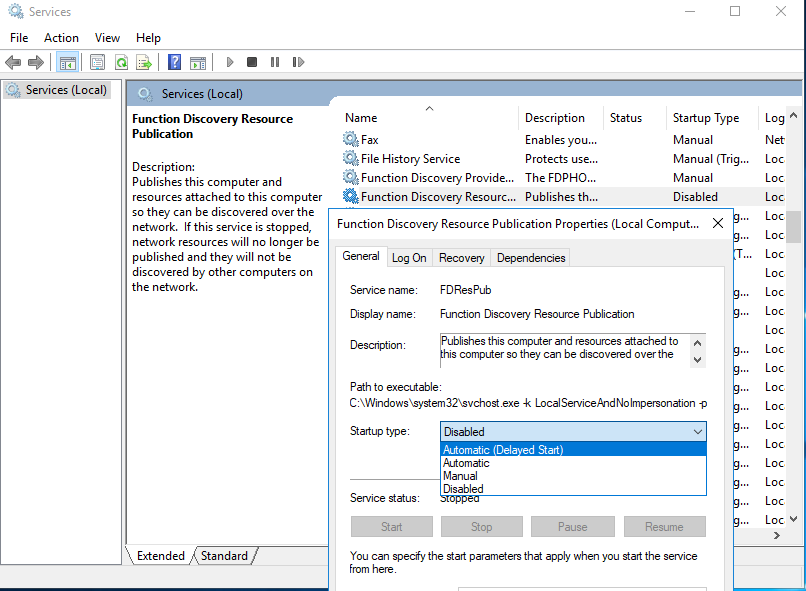
- Open the Windows Services Management console (
services.msc); - Change the service startup type from Manual to Automatic (Delayed Start)
- In the list of services, find the Function Discovery Resource Publication service;
- In the same way, enable the Function Discovery Provider Host service;You can set these services to start automatically with the following one-line PowerShell:
get-Service fdPHost,FDResPub|Set-Service -startuptype automatic -passthru|Start-Service - Restart your computer
After rebooting, other computers on the local network will be able to discover this computer and its resources (shared network printers and folders).
Computer Browser Service and SMB 1.0 Protocol in Windows 10/11
It happens that problems with displaying computers in a network environment are related to the Computer Browser service. This service is responsible for generating and maintaining a list of active computers on the local network. There can be only one active computer with the Master Browser role on a local network.
You can identify the current Master Browser host in your network by running the following command on each computer in your network:
nbtstat -a ComputerName
The computer that is the Master Browser is the only one that has the value __MSBROWSE__.
On Windows 10 1703, the Computer Browser service works incorrectly. It is recommended to completely disable this service on Windows 10 and use the computer with Windows 8.1/Windows Server 2012 R2 as the Master Browser on your network. You can set the Master Browser computer via the registry.
In addition, in Windows 10 1709 and newer (1803 up to 21H2), the Computer Browser service and the SMB v1.0 protocol are disabled by default. The Computer Browser service is responsible for building a list of computers on the network and displaying them (this discovery protocol is widely used before switching to the SSDP and WS-Discovery protocols).
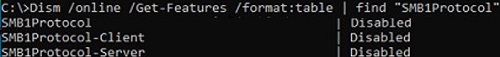
You can check the status of the SMBv1 protocol on your computer using the command:
Dism /online /Get-Features /format:table | find "SMB1Protocol"
If you have only computers running Win 10 1709 and newer in your local network (see the table of SMB versions), and you still want to use the Computer Browser, you will have to enable the SMB v1.0 protocol on at least one computer (it’s not safe!). This computer will be used as the Master Browser on your network.
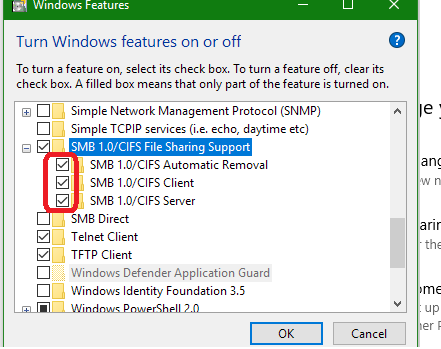
You can enable the SMB 1.0 support by enabling the following Windows features from the Control Panel (OptionalFeatures.exe):
- SMB 1.0 /CIFS Client;
- SMB 1.0 /CIFS Server.
Or you can enable SMB 1.0 features with the DISM commands:
Dism /online /Enable-Feature /FeatureName:"SMB1Protocol-Client"
Dism /online /Enable-Feature /FeatureName:"SMB1Protocol-Server"
If you enabled the SMB1 protocol, then in order to set the current computer as the Master Browser on the network, run the following commands:
reg add "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Browser\Parameters" /v IsDomainMaster /t REG_SZ /d True /f
reg add "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Browser\Parameters" /v MaintainServerList /t REG_SZ /d Yes /f
This computer will be the Master Browser in your network.
Cannot See Shared Folders from a Windows Device
In some cases, Windows 10 can see and explore a neighboring device in a workgroup environment, but cannot display a list of shared network folders on it. This is most often accompanied by the error “0x80070035 – Network path not found”. The solution to this problem is described in this article.
If a neighboring computer (device) is visible on the network, but when you try to open any shared network folder from the Network Neighborhood or by the UNC path (\\Hostname_or_IP), an error appears “You can’t access this shared folder because your organization’s security policies block unauthenticated guest access”. In this case, you need to enable the AllowInsecureGuestAuth registry parameter using the command (for details, see the article Can’t Access Shared Folder on Windows 10):
reg add HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanWorkstation\Parameters /v AllowInsecureGuestAuth /t reg_dword /d 00000001 /
If all else fails and the computers are still not visible in the local network environment:
- Turn off all computers and restart your router or Wi-Fi access point;
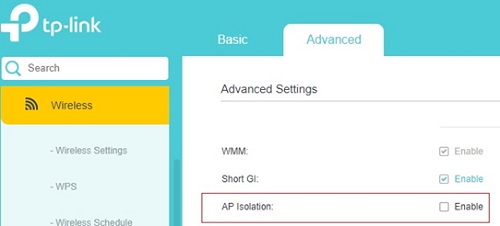
- If your LAN is based on a Wi-Fi router, check if the client isolation feature is disabled on it(wireless isolation, client isolation, or AP isolation).In TP-Link Wi-Fi routers, this option is located in the “Advanced Settings” section;
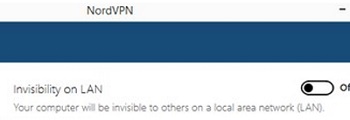
- If your computer has an active VPN connection, try disconnecting it and checking for network discovery on your local network;
- If your computer has several active network interfaces (for example, Wi-Fi and Ethernet), try to disable all interfaces except those connected to the local network with other devices;
- Try temporarily disabling your antivirus and/or firewall software;
- Disable the IPv6 protocol in the properties of your network connection;
- Check the availability of computers in your LAN using standard Windows tools:
ping IPorping hostname